Hives (Urticaria)
Hives (Urticaria)
Book Now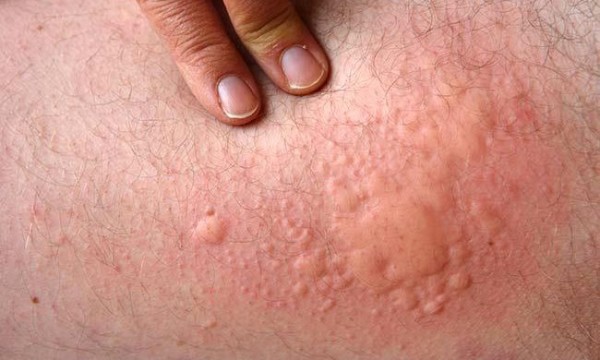
Hives (Urticaria)
What is Angioedema?
Angioedema is a form of urticaria that occurs deeper in the skin, resulting in swelling, itching, or a burning or tingling sensation. It often affects areas such as the eyelids, lips, and sometimes the mouth. When the hands are affected, the swelling can be painful. If the mouth is involved, it can lead to severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing and swallowing. Angioedema and urticaria can occur separately, or together.
What Causes Urticaria and Angioedema?
The cause of both conditions is the release of histamine from allergy cells (mast cells) in the skin. Physical factors such as exercise, pressure on the skin, or cold, as well as foods, medications, and infections can trigger the release of histamine from these cells. In some cases of chronic urticaria, the body's immune system (autoantibodies) may stimulate mast cells in the skin to release histamine. In typical cases of urticaria, no specific cause is usually identified.
What Triggers Urticaria (Hives)?
The following factors can trigger urticaria:
- Infections: Particularly upper respiratory infections like colds and the flu.
- Medications: Any medication can potentially cause hives, but painkillers, muscle relaxants, and antibiotics are more commonly implicated. Some blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors) can cause angioedema.
- Alcohol, Foods, and Food Additives: Rarely, certain foods such as nuts, fish, tomatoes, and strawberries can trigger urticaria.
How Can I Prevent Urticaria?
The most important measure to prevent hives is to avoid the triggers that can worsen the condition. These include:
- Painkillers: Avoid using painkillers unless necessary (paracetamol is generally considered safe for this purpose), and avoid aspirin.
- Blood Pressure Medications: ACE inhibitors, used to treat high blood pressure, should be avoided in patients with angioedema.
- Alcohol: Avoid alcohol consumption.
- Exercise and Environmental Conditions: Avoid intense physical exercise and extreme temperatures (either too hot or too cold).
- Food Additives: Avoid foods that contain artificial colorings and additives.
How is Urticaria Treated?
The most important aspect of treating urticaria is avoiding the triggers that worsen the condition. The following medications are commonly used:
-
Antihistamines: These are the primary drugs used to treat itching and swelling. They work by preventing the release of histamine and can help control the symptoms. It's essential to take these medications regularly (even when there are no visible hives), as consistent use helps achieve the best results. If the condition is not well-controlled, your doctor may increase the dosage. Some antihistamines can cause drowsiness or concentration problems, while others cause less sleepiness. However, taking them with alcohol may also cause drowsiness. If you work in jobs requiring focus, drive, or need mental alertness, inform your doctor. Depending on the duration of the illness, long-term use of these medications may be necessary.
-
Steroids and Immunosuppressive Drugs: In more severe or resistant cases, steroids and drugs like cyclosporine, which affect the immune system, may be used. Additionally, injectable medications like omalizumab may be recommended.
Emergency Symptoms:
Swelling of the tongue and throat is not common but can be a sign of angioedema. Although rare, this can be life-threatening. If you experience these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention at the nearest healthcare facility.
Make an Appointment
The best way to enjoy a treatment at our salon is to book an appointment with the desired esthetician. Fill in the form below and we will contact you to discuss your appointment.