Seborrheic eczema
Seborrheic eczema
Book Now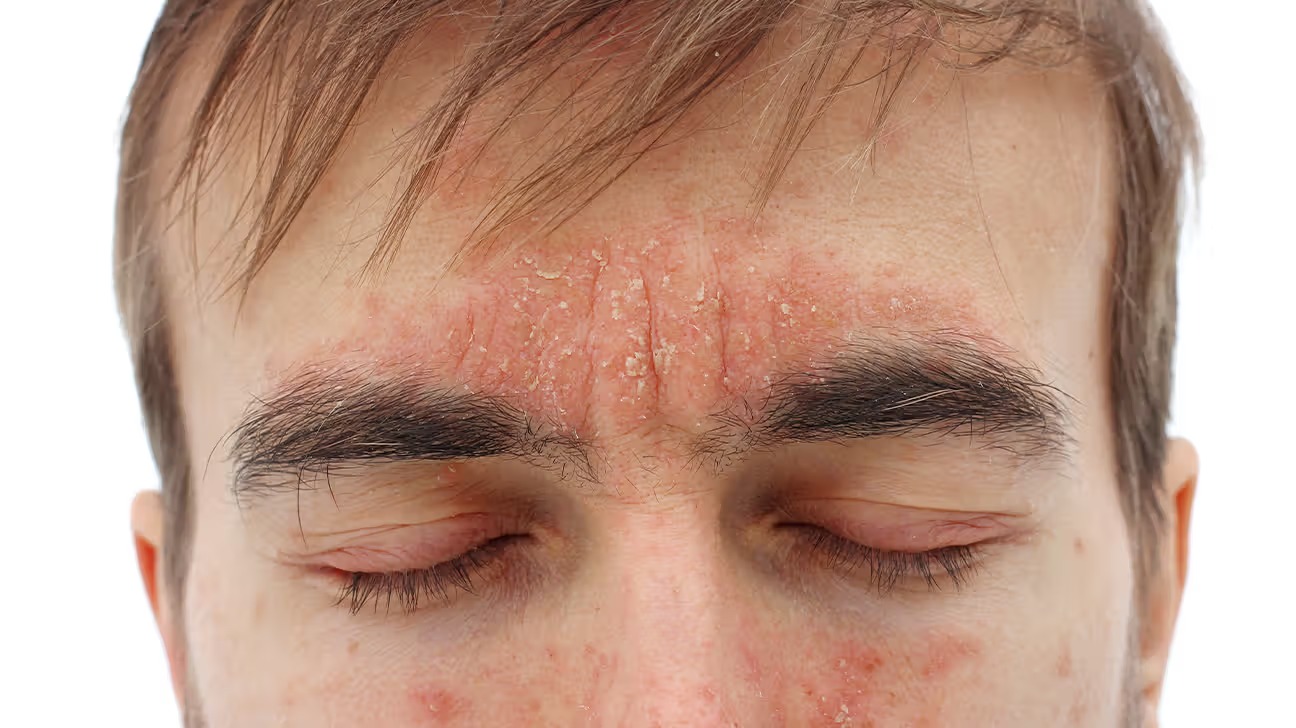
Seborrheic eczema
Seborrheic eczema
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common, non-contagious, and easily manageable skin condition. It causes red, itchy patches and greasy scales on the skin, which can often result in white or yellow flaking on the scalp. Seborrheic dermatitis is the same condition known by various names such as dandruff, seborrheic eczema, or sebopsoriasis. When it occurs in infants, it is referred to as "cradle cap."
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis isn't fully understood, but it is thought to be related to an overgrowth of yeast (Malassezia), which normally lives on the skin. The condition may also be influenced by hormonal changes, immune system responses, or environmental factors. Although it can resolve without treatment, some individuals may need long-term use of medicated shampoos or topical treatments to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Affected Areas of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis typically appears in areas of the body with high concentrations of oil-producing (sebaceous) glands. These areas include:
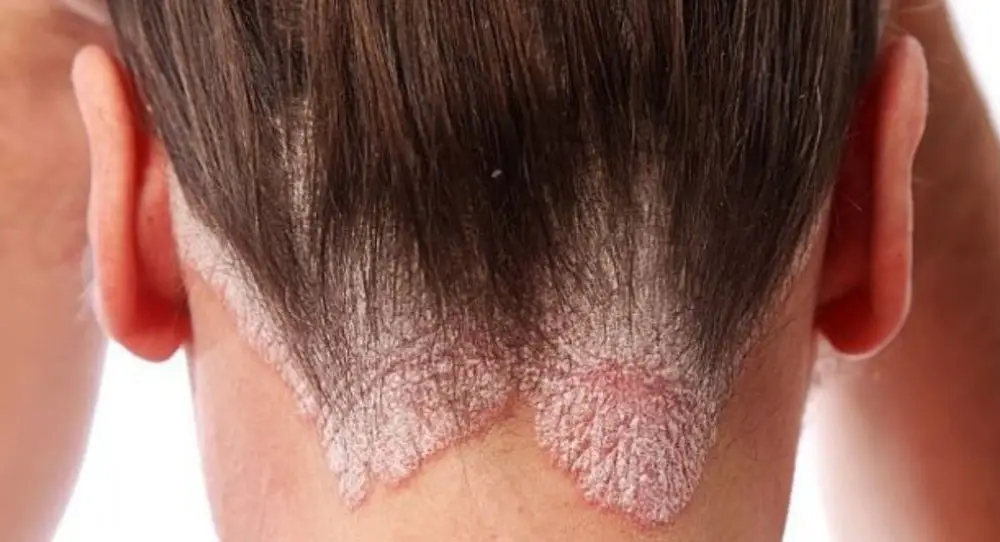
- Scalp: One of the most common areas affected by seborrheic dermatitis is the scalp, which can become inflamed and covered with flaky, oily patches. People with oily skin are more prone to developing scalp issues, such as dandruff, due to the overactivity of sebaceous glands.
- Eyebrows: This condition can manifest as dandruff in the eyebrows, leading to flakiness and irritation.
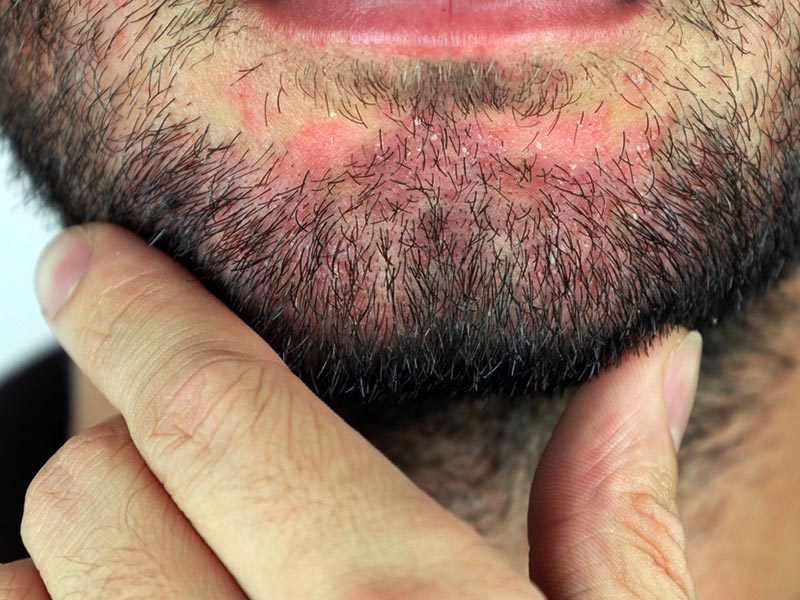
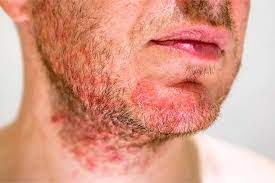
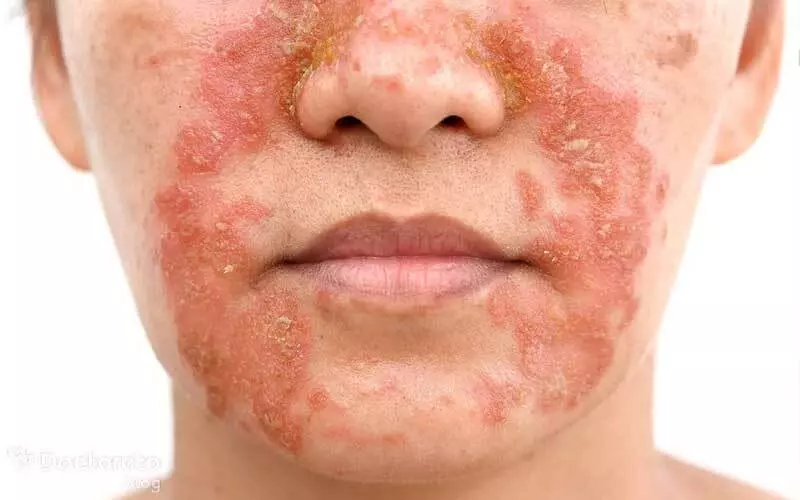
- Face: Seborrheic dermatitis of the face often results from the overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, leading to inflammation and changes in the skin's appearance. It can affect areas like the forehead, cheeks, and nose folds. Men are more commonly affected than women, particularly in their third or fourth decade of life.
- Under the Breasts: In individuals with lighter skin, red patches may appear under the breasts, while in those with darker skin, lighter spots may be visible.
- Chest: Seborrheic dermatitis may also develop on the upper chest, leading to red, flaky rashes.
- Ears: The condition can spread to areas around and behind the ears. Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids and antifungal creams, are often prescribed to alleviate these symptoms.
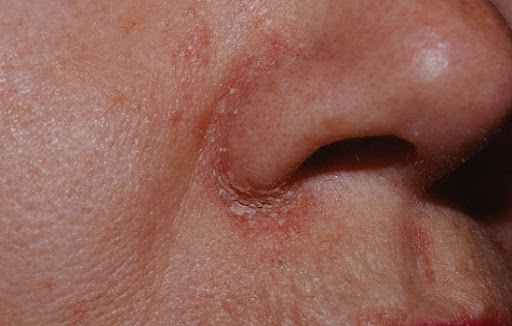
- Nose: Factors such as topical steroid use, cosmetic products, and hormonal changes can trigger seborrheic dermatitis around the nose.
- Armpits: Though seborrheic dermatitis predominantly affects the scalp, it can also appear in the armpits, characterized by red, scaly patches that may be itchy.
- Groin: In the groin area, seborrheic dermatitis results in red, itchy, flaky patches, commonly affecting areas such as the genitals and anus.
Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Common symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include:
- Scalp scaling: Often appearing in the form of dandruff, this is one of the most common symptoms.
- Flakiness on facial areas: Such as around the nose, eyebrows, and behind the ears.
- Patches of greasy skin covered in flaky white or yellow scales.
- Redness or discoloration in affected areas, especially for individuals with lighter skin tones.
- Itching in the scalp, face, chest, and groin areas.
Seborrheic Dermatitis in Infants
In infants, seborrheic dermatitis is commonly known as cradle cap, which results in thick, crusty, and sometimes greasy scales on the scalp. While cradle cap is not a severe condition, it can cause yellow or white patches to develop on the scalp. In some infants, the condition may spread to the diaper area, face, neck, or trunk.
Seborrheic Dermatitis in Children
This condition is relatively common in children. It appears as flaky, itchy skin with white, yellow, or red patches, primarily on the scalp, though it can also affect the face.
Seborrheic Dermatitis in Adults
When seborrheic dermatitis occurs in adults, it often persists for years, and in some cases, throughout a person's lifetime. Treatments may not offer a permanent cure, but they can help reduce the symptoms, such as itchiness, redness, and swelling. Seborrheic dermatitis in adults typically follows a pattern of flare-ups and remissions, making long-term management necessary for most individuals.
Conclusion
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition that can be managed but not cured. While it can affect people of all ages, it is particularly prevalent in adults and infants. The condition is associated with overactive sebaceous glands and the presence of the Malassezia yeast on the skin. Treatments, including medicated shampoos, antifungal creams, and topical corticosteroids, can help control symptoms and reduce flare-ups, though the condition may return periodically throughout a person's life.
Make an Appointment
The best way to enjoy a treatment at our salon is to book an appointment with the desired esthetician. Fill in the form below and we will contact you to discuss your appointment.