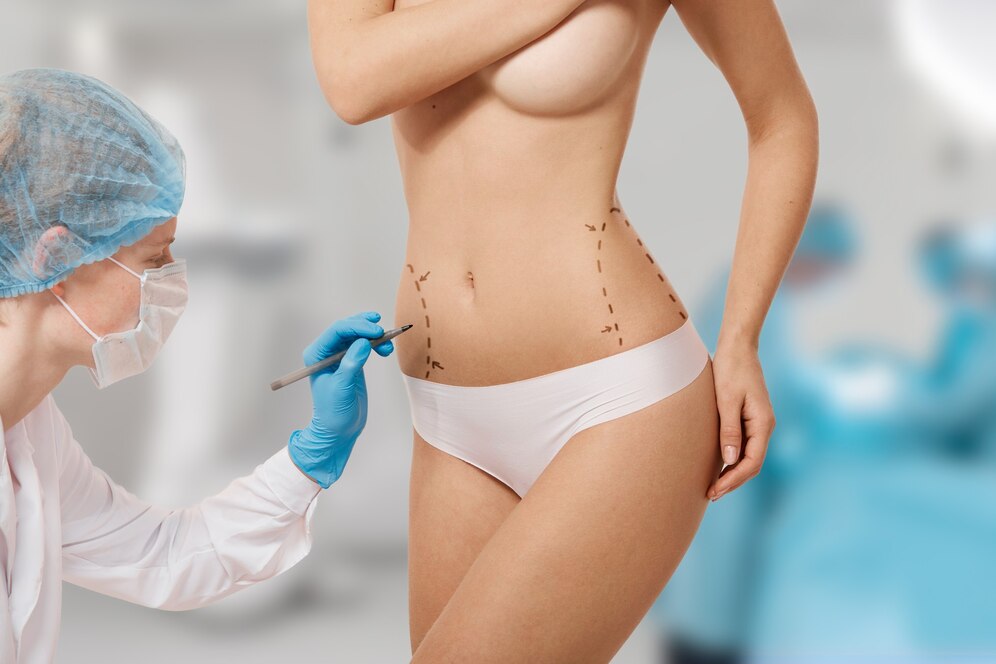
In the pursuit of a toned, athletic body, abdominal muscle definition has become a popular aesthetic goal. For those who find it challenging to attain a six-pack or toned abdominal muscles despite rigorous diet and exercise, abdominal muscle aesthetic surgery has emerged as a sought-after solution. Both men and women seek these surgeries, which are designed to create a more defined, muscular abdomen through techniques such as liposuction, fat grafting, and occasionally skin tightening. Known as six-pack surgery for men and two-pack surgery for women, these procedures offer a shortcut to a fit, sculpted appearance.
What Is Abdominal Muscle Aesthetic Surgery?
Abdominal muscle aesthetics involves creating a visibly toned stomach by surgically sculpting the abdominal muscles. These surgeries are particularly appealing to individuals who, despite a disciplined diet and workout routine, are unable to achieve the muscle definition they desire due to genetic predispositions or other factors. Six-pack surgery is generally targeted at men and creates the classic “six-pack” appearance with six symmetrical bulges. Meanwhile, two-pack surgery is popular among women and focuses on defining the two muscles along the central line of the abdomen, resulting in a feminine yet athletic look.
By utilizing a combination of liposuction and fat grafting, the abdominal muscles are contoured to form the desired shape. Both procedures can deliver a natural, muscular look without noticeable scars, as modern techniques avoid extensive skin incisions.
How Does the Procedure Work?
The six-pack and two-pack surgeries employ similar principles with some distinctions based on the desired muscle definition. Both procedures start with a consultation to understand the patient’s aesthetic goals and assess their overall health. Candidates must be in good health, generally over 18 years of age, and ideally, not obese. Patients with systemic health conditions are required to get clearance from their healthcare provider before proceeding.
The surgeries are typically performed under either sedation or general anesthesia. The surgeon begins by outlining the desired muscle shape on the abdomen using temporary markings to guide the procedure. Liposuction is used to remove excess fat along the natural contours of the muscles, highlighting the abdominal shape. For some patients, the surgeon will extract fat from other areas of the body and strategically inject it into specific parts of the abdomen to enhance the muscle definition.
In cases where there is loose skin or significant sagging, additional procedures like skin tightening or tummy tucks may be recommended to ensure a firm, youthful look.
Six-Pack Surgery for Men
Men seeking six-pack surgery often aim to achieve a visibly muscular appearance with six distinct “blocks” of abdominal muscles. This procedure involves removing fat deposits around the muscle lines through liposuction, followed by precise fat grafting. The surgeon enhances the lines dividing the six abdominal muscles and accentuates the natural dips and curves, creating a defined, masculine contour.
For men who work out regularly, the results can amplify their muscular efforts and maintain a consistent appearance, complementing their fitness routine without long hours at the gym.
Two-Pack Surgery for Women
Two-pack surgery, a popular choice for women, focuses on a more subtle, elegant abdominal contour. Women generally aim for a toned, flat abdomen rather than the pronounced six-pack look often sought by men. This procedure emphasizes the central vertical line and highlights the two parallel muscles on either side of this line, often using less extensive fat removal and reshaping.
Women who may have experienced changes in their abdominal area due to factors like pregnancy or hormonal fluctuations often choose two-pack surgery to regain a defined, athletic midsection. The results can help restore confidence and create a harmonious, feminine physique.
What to Expect After Surgery: Recovery and Results
Recovery time for six-pack and two-pack surgeries is typically swift, allowing patients to return to daily activities within a week or two. Post-surgery, a compression bandage is usually applied to support the abdomen and reduce swelling. Mild discomfort, redness, and bruising may be present for the first few days. Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting, intense physical activity, and any pressure on the abdominal area for at least four weeks.
Final results begin to become visible within a few weeks, and the desired muscle definition is fully apparent in about three months. Patients are encouraged to maintain a stable weight and consistent fitness regimen to preserve the surgical outcomes. Major weight fluctuations can diminish the muscle definition achieved through the surgery.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate?
Abdominal muscle aesthetics can benefit both men and women who are over 18, have completed their physical development, and are in good health. This surgery is ideal for individuals who have tried to achieve muscle definition through diet and exercise without success. The procedure is also suitable for people who want to enhance their physique without investing years into physical training.
However, individuals with certain health conditions may need special considerations, and consultations with an experienced surgeon are essential to ensure the procedure is safe and effective for them.
Cost Considerations for Six-Pack and Two-Pack Surgeries in 2024
Abdominal muscle aesthetics can vary in cost depending on factors like the surgeon’s experience, the amount of liposuction required, and any additional procedures. Patients should opt for accredited, reputable clinics with experienced cosmetic surgeons to minimize risks and ensure high-quality care. In Turkey, for instance, a thriving center for medical tourism, costs may be relatively lower than in Western countries. However, pricing still reflects factors like the complexity of the surgery, materials used, and follow-up care required.
Choosing a Qualified Surgeon
Given the technical demands of abdominal muscle aesthetics, selecting a qualified, board-certified cosmetic surgeon is crucial. An experienced surgeon will guide patients through the procedure, set realistic expectations, and offer post-surgical care instructions to optimize results.
The Growing Popularity of Abdominal Muscle Aesthetic Surgery
As the demand for a toned, muscular body continues to grow, abdominal muscle aesthetics have become increasingly accessible. These procedures offer a streamlined, efficient way to achieve the “ideal” look with minimal recovery time and long-lasting results. Men and women alike are embracing six-pack and two-pack surgeries as viable options to enhance their physical appearance and boost self-confidence.
In summary, six-pack and two-pack abdominal surgeries offer a promising path to a defined, fit-looking body that resonates with today’s aesthetics-focused fitness goals. By consulting with skilled cosmetic professionals, patients can transform their appearance safely and enjoy the look of a toned, muscular abdomen without years of gym dedication.
frequently asked questions (FAQs)
1. What is six-pack surgery?
Answer: Six-pack surgery, also known as abdominal muscle surgery, is a cosmetic procedure designed to enhance the appearance of the abdominal muscles. It involves the removal of excess fat through liposuction and the injection of fat or the use of implants to create a more defined and sculpted abdominal area. This surgery is popular among individuals who struggle to achieve their desired abdominal appearance through diet and exercise alone.
2. Who is a suitable candidate for six-pack surgery?
Answer: Ideal candidates for six-pack surgery include both men and women who are over 18 years old, have completed their body development, and are in good overall health. Individuals who have tried to achieve visible abdominal muscles through diet and exercise without success, or those who want to enhance their athletic appearance, may benefit from this procedure. However, those with chronic health conditions should consult with their doctors for clearance before undergoing the surgery.
3. How is the surgery performed, and what is the recovery process like?
Answer: Six-pack surgery is typically performed under sedation or general anesthesia. The procedure involves marking the desired abdominal muscle outlines on the patient's body. Excess fat is removed using liposuction, and then the removed fat is injected into specific areas to create a more pronounced muscle definition. The recovery process is relatively quick; patients usually see initial results within a few weeks. Light swelling and redness in the treated area are normal and typically resolve as healing progresses. Patients are advised to maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine post-surgery to preserve their results.
4. Are there any risks or complications associated with six-pack surgery?
Answer: As with any surgical procedure, six-pack surgery carries some risks, including infection, scarring, and complications related to anesthesia. There may also be the potential for uneven results if the fat is not injected properly. Choosing an experienced and qualified plastic surgeon can help minimize these risks. Patients are encouraged to follow all pre-operative and post-operative instructions provided by their surgeon to ensure a safe and successful outcome.
5. What are the costs associated with six-pack surgery in 2024?
Answer: The cost of six-pack surgery can vary significantly based on several factors, including the surgeon's experience, the amount of liposuction performed, the type of materials used, and the specific techniques employed. As of 2024, prices may range widely, and patients are advised to consult with their chosen plastic surgeon to get a detailed quote. It’s important to consider that this is not a simple procedure; patients should seek facilities that provide comprehensive care and have experienced surgical teams to ensure the best results.