Psoriasis (Psoriatic Disease)
Psoriasis (Psoriatic Disease)
Book Now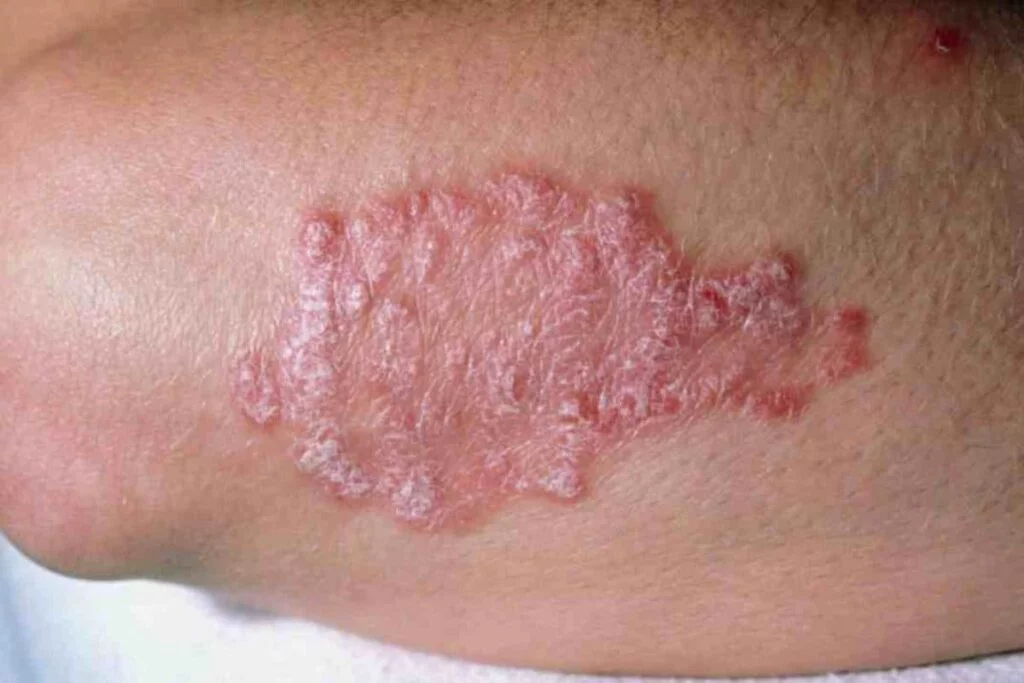
Psoriasis (Psoriatic Disease)
Psoriasis is a common, chronic skin condition that often persists for long periods with flare-ups. The lesions typically appear as sharply defined red patches covered with silvery scales (which give the condition its name "psoriasis").
What are the causes of psoriasis?
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of immune system dysfunction, genetic factors, and environmental triggers. Environmental factors such as streptococcal throat infections, certain medications (e.g., corticosteroids, lithium, some blood pressure medications, aspirin, etc.), excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, scratching, scrubbing the skin, sunburn, and psychological stress can initiate or exacerbate the condition.
Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is not contagious and cannot be spread through physical contact.
What is the course of psoriasis?
Psoriasis is generally a chronic condition that follows a pattern of flare-ups and periods of remission. The severity and symptoms can vary from person to person and may even change over time in the same individual.
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
Diagnosis is typically made based on clinical findings. In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary for confirmation.
How is psoriasis treated?
There is no definitive cure for psoriasis, but with appropriate treatment, the disease can be controlled, and long-term remission may be achieved. Treatment selection and duration depend on several factors, including the extent of the disease, its location, involvement of nails or joints, and more. Treatment requires close collaboration between the physician, patient, and their family. It is essential to avoid triggers that could worsen the condition, such as scratching, scrubbing the skin, or using harsh products.
For localized psoriasis, topical treatments are often used, including medications that remove scales from the skin, corticosteroids, anthralin, calcipotriol (synthetic vitamin D), and calcineurin inhibitors. These treatments can be used in combination. In cases of resistant or widespread disease, systemic treatments such as methotrexate, cyclosporine-A, acitretin (synthetic vitamin A), and phototherapy may be prescribed. If these treatments are ineffective, biologic agents (such as adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, ustekinumab, etc.) may be considered.
The success of treatment depends not only on the dermatologist's expertise and experience but also on the patient's adherence to the prescribed therapy.
"If you have a skin condition, consult a dermatologist. Trust your skin to a specialist."
Make an Appointment
The best way to enjoy a treatment at our salon is to book an appointment with the desired esthetician. Fill in the form below and we will contact you to discuss your appointment.